AKS Cluster Part.3
Published Date: 04-FEB-2019
In Part 2, we setup a private Azure Container Register using azure-cli and terraform.
For the 3rd and final instalment of this "Look Ma, I'm playing with Azure!", we will deploy an application to our AKS cluster using kubectl
Series Overview
- Part 1 - get Kubernetes cluster up and running on Azure Kubernetes Managed Service (AKS)
- Part 2 - create a private Docker Registry in the cloud using Azure's Container Registry Managed service (ACR)
- Part 3 - deploy a simple application to AKS.
Pre-requisites tools
Get these installed if you haven't already:
- Azure portal account
- Azure az-cli (command line interface)
- Terraform installed (zipped binary, copy to ~/bin)
- Kubectl installed
Right, quick run through the new ACR setup so that the rest of the code below is relevant to that:
(new) AKS cluster deployed
I have updated Part 1 so if you've followed that you should be up to speed at this point.
Make sure you have your kubeconfig file handy for the 'helm' section!
run this to get your kubeconfig: $ az aks get-credentials --resource-group AKS-CLOUDRESOURCES --name AKS-cloudbuilderio
(new) Azure Container Registry
Part 2 has also been updated, so hopefully you have a running AKS cluster AND a working Azure Container Registry now!
Right. We are ready to deploy something to our AKS cluster!
K8s Deployment
This file basically uses 'kubectl' to deploy whatever we specify in here, as "pods" in our cluster (note kubectl by default will point to whatever you have in ~/.kube/config)
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.8
ports:
- containerPort: 80
kubectl: deploy
$ kubectl apply -f ./deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/nginx created
kubectl: check deployment
$ kubectl get deploy
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx 2 2 2 2 81s
kubectl: check pods
$ kubectl get pods -lapp=nginx -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE
nginx-5cd6d46846-cr5m7 1/1 Running 0 6m10s 10.244.0.9 aks-nodes-28201024-2 <none />
nginx-5cd6d46846-ntszh 1/1 Running 0 6m10s 10.244.2.3 aks-nodes-28201024-1 <none />
K8s Service
Again, like the deployment this is just a basic "service" component to be deployed. A Service is an abstraction that defines a set of pods somewhere on your cluster that all do the same thing. If a node dies and takes all the pods with it, as long as there was a 'Service' configured for the functionality of those pods, the new pods that come up with new IP addresses will be known to the Service.
$ kubectl apply -f service.yaml
service/nginx created
check our service is up & running
$ kubectl get svc nginx
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx ClusterIP 10.0.154.171 <none /> 80/TCP 24s
Delete deployment
$ kubectl delete deploy nginx
deployment.extensions "nginx" deleted
Deploy NGINX yaml
Okay, you get the idea pretty much you can kubectl 'apply' yaml files of deployments and services to your AKS cluster as easy as that.
So for our grand finale, we will do an nginx deploy we can actually get to from the internet.
nginx.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
run: nginx
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
selector:
run: nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
run: nginx
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: registercloudbuilderio.azurecr.io/nginx:1.8
ports:
- containerPort: 80
use our own azurecr.io (container registry)
let's pull the image from our own ACR instead
prepare our image
pull from docker hub.
$ docker pull nginx:1.8
1.8: Pulling from library/nginx
efd26ecc9548: Pull complete
a3ed95caeb02: Pull complete
24941909ea54: Pull complete
7e605cb95896: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:c97ee70c4048fe79765f7c2ec0931957c2898f47400128f4f3640d0ae5d60d10
Status: Downloaded newer image for nginx:1.8
re-tag
docker tag nginx:1.8 registercloudbuilderio.azurecr.io/nginx:1.8
push to our ACR.
$ docker push registercloudbuilderio.azurecr.io/nginx:1.8
The push refers to repository [registercloudbuilderio.azurecr.io/nginx]
5f70bf18a086: Pushed
62fd1c28b3bf: Pushed
6d700a2d8883: Pushed
c12ecfd4861d: Pushed
1.8: digest: sha256:746419199c9569216937fc59604805b7ac0f52b438bb5ca4ec6b7f990873b198 size: 1977
deploy nginx.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f ./nginx.yaml
service/nginx created
deployment.apps/nginx created
do a describe on the pods to verify it pulled the image we pushed to ACR
$ kubectl describe pods nginx-66867b8df4-kzbd2
...
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 28s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/nginx-66867b8df4-kzbd2 to aks-nodes-28201024-0
Normal Pulling 26s kubelet, aks-nodes-28201024-0 pulling image "registercloudbuilderio.azurecr.io/nginx:1.8"
Normal Pulled 10s kubelet, aks-nodes-28201024-0 Successfully pulled image "registercloudbuilderio.azurecr.io/nginx:1.8"
Normal Created 10s kubelet, aks-nodes-28201024-0 Created container
Normal Started 9s kubelet, aks-nodes-28201024-0 Started container
looks good!
port-forward (cheating)
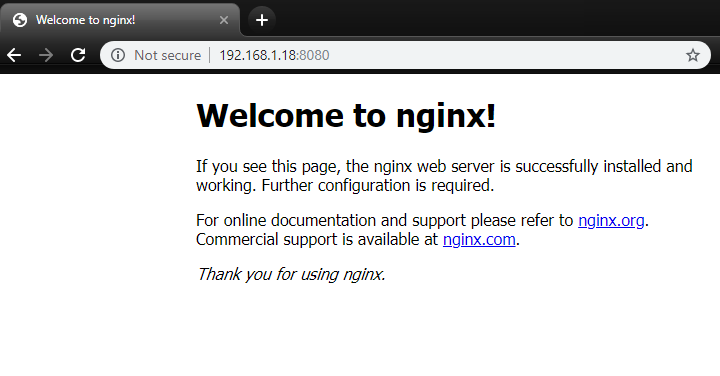
A quick way to check the app (nginx) is serving correctly is to port-forward a local port to the AKS cluster and into the nginx pods.
Here is how I had to do it because I run my kubectl from a linux vm, so I serve the port-forward on that vm and connect to it from this (windows) PC.
kubectl port-forward --address 0.0.0.0 deployment/nginx 8080:80
what this does
- forwards traffic to the
nginxdeployment - serves it locally via
0.0.0.0(made available via a 192.x.x.x local ip) - serves locally on port
8080and forwards through to port80on the nginx deployment.
tada!
Thanks for following along and if you see anything that needs updating/correcting etc. please feel free to let me know!
References
-
HTTPS ingress for AKS (Ive just got this here for future refernce when I want to come back and do this properly.)