EC2 Associate Level
note
In Stephane Marek's course, this chapter was calling out "associate level" EC2 details.
info
These were the topics I created flashcards for (Remnote) and would revise them using spaced repetition. The formatting is an export from Remnote.
- Public vs Private IP
- Public
- unique in public
- easily moved specific geo
- Private
- unique in private network
- can be same in different private networks
- instances need NAT + IG to reach public internet
- Public
- Elastic IP
- is a public IP
- provides a fixed IP for your instance
- restart may change public IP
- attached to single instance
- 5 Elastic IP per account (can request more)
- Best Practice
- Avoid using EIP―Use random IP + register DNS, or LB instead
- Placement Groups
- What are the 3 Placement Group "strategies"? ↓
- Cluster
- Partition
- Spread
- What's the goal of Placement Groups?―Spread instances over different underlying hardware to minimise risk of concurrent failures.
- Cluster
- all instances
- single AZ
- single rack
- low-latency network performance (10gb)
- riskiest due to no {{redundancy}} if single rack or AZ {{fails}}
- what kind of applications is a cluster placement group good for?―High Performance Computing (HPC)
- all instances
- Partition
- instances
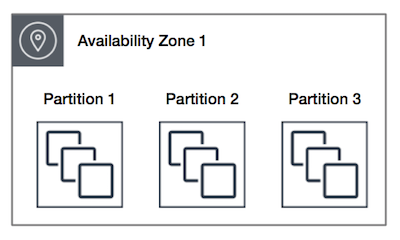
- multi-AZ in single Region
- can do 2 x partitions in 1 x AZ and 1 x in another
- 7 partitions per AZ
- partitions don't share racks with other partitions
- what popular DBMS are ideal to use 'Partition' placement groups (hint: H H C K)?―HDFS, HBase, Cassandra, Kafka
- instances
- Spread
- instances
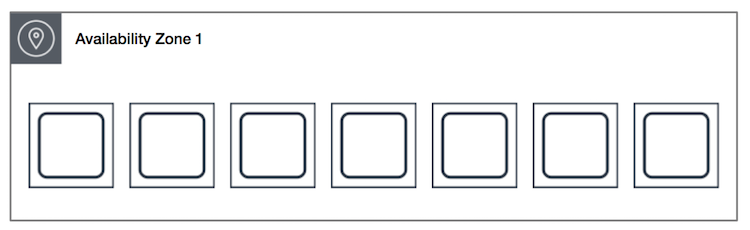
- separate hardware
- multi-AZ
- 7 x VM per AZ per Placement Group
- use case: {{critical}} applications reduce risk of {{simultaneous}} failures.
- instances
- What are the 3 Placement Group "strategies"? ↓
- Elastic Network Interface (ENI)
- possible attributes
- primary (private) IPv4 + secondary IPv4
- 1 x EIP per private IPv4
- can move them from Ec2 to Ec2
- bound to AZ
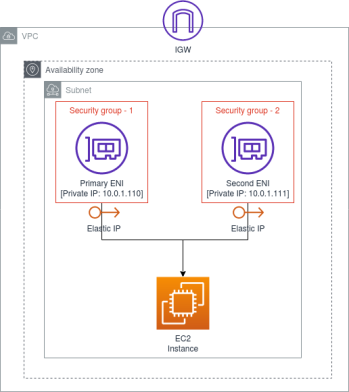
- possible attributes
- EC2 Hibernate
- RAM state preserved
- state written to root EBS volume
- root EBS volume must be encrypted
- AMI must be encrypted
- hibernate is good for...?― ↓
- long-running process
- speed up instance initialise time because its not "starting up" from scratch, its loading from point-in-time state.
- RAM size must be < 150GiB
- Available for which Instance Types?―On-Demand, Reserved and Spot instances
- EC2 Nitro
- better performance "similar to bare metal"
- High-speed EBS
- Nitro 64,000 EBS IOPS
- Non-Nitro max 32,000
- better (underlying) security
- EC2 vCPU
- multi-threading
- each thread = vCPU
- maths: 4 x CPU running 2 threads per CPU = 8 vCPUs
- Options
- decrease # of CPU cores to decrease license costs
- turn off multi-threading good for HPC workloads
- EC2 Capacity Reservations
- long-term commitment not required (1 & 3)
- capacity access & billing are immediate
- required specs ↓
- AZ
- number of instances
- instance attributes e.g. type, tenancy, OS
- cost savings if combined with RI's and Savings Plans