AWS EKS Networking Best Practices - VPC CNI and Container Networking
These are my notes on "Amazon EKS Best Practices Guide for Networking"
Network Model
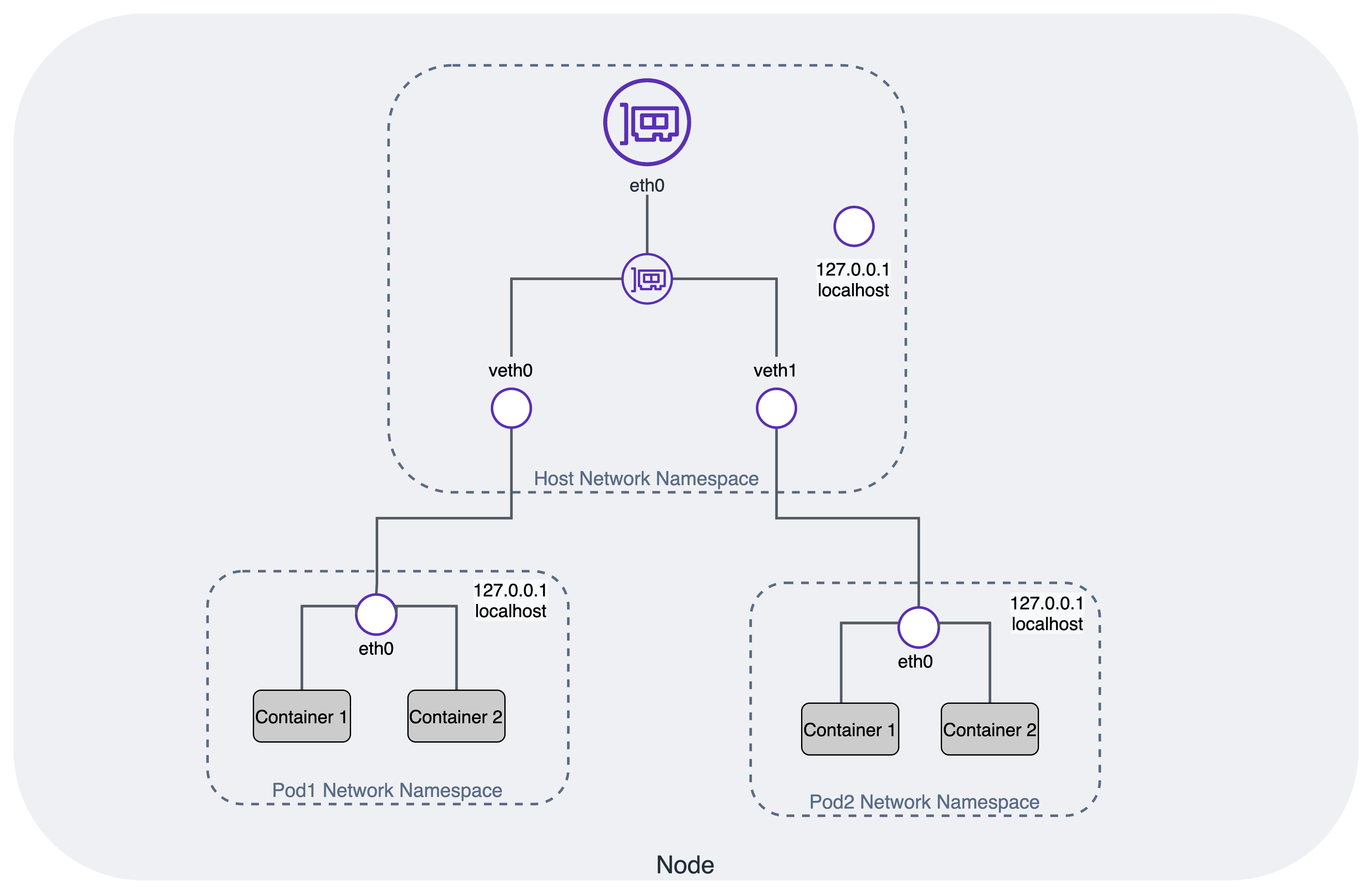
Container Network Interfce (CNI)
The CNI plugin is enabled by passing kubelet the --network-plugin=cni command-line option. Kubelet reads a file from --cni-conf-dir (default /etc/cni/net.d) and uses the CNI configuration from that file to set up each Pod’s network.
Amazon VPC CNI
I was going through this section, thinking, this doesn't all need to be known, chatgpt summarise this and pull out key parts, and make an analogy to make it easier to remember.
Visual Summary
1. Default Setup:
- VPC CNI is the default networking add-on for EKS clusters.
- Components:
- CNI Binary: Assigns IPs to Pods.
- ipamd Plugin: Manages ENIs and IP pools.
2. IP Management:
- Secondary IP Mode (Default):
- Allocates IPs from node subnets.
- Suitable for small clusters.
- Prefix Mode:
- Assigns prefixes to ENIs for higher pod density.
3. Networking Best Practices:
- Integrates with AWS VPC networking/security.
- Uses primary ENI security group for Pods.
- Security Groups for Pods: Enable for distinct network rules per Pod.
4. Handling IPv4 Address Exhaustion:
- Custom Networking: Use CG-NAT CIDRs to save VPC IPs.
- Secondary CIDRs: Extend available IPs.
- IPv6: Preferred long-term solution, assigns IPv6 addresses to Pods.
Analogy
Imagine you're organizing a massive conference (EKS cluster):
-
VPC CNI is the event's default management team.
- CNI binary: Assigns seats (IP addresses) to attendees (Pods).
- ipamd plugin: Manages rooms (ENIs) and keeps a list of available seats.
-
Secondary IP Mode (default): Suitable for small events. Uses existing rooms and seats.
-
Prefix Mode: For larger events, assigns blocks of seats to rooms for better organization.
-
Networking Best Practices:
- Use venue's (AWS VPC) established security and traffic rules.
- Apply venue’s main security to all attendees, with the option to customize rules for specific groups.
-
Handling Seat Shortage:
- Custom Networking: Utilize alternative seating arrangements (CG-NAT CIDRs).
- Secondary CIDRs: Extend available seating.
- IPv6: Preferred solution, assigns new types of seats (IPv6) for future-proofing.
This helps visualize how VPC CNI manages IPs and adapts to scaling challenges in EKS clusters.
Optimise IP Utilisation
Recommendations for Optimizing IP Address Utilization in Amazon EKS
-
Prefix Delegation:
- Use prefix delegation to assign IPv4 or IPv6 prefixes to Amazon EC2 instances.
- Increases IP addresses per ENI, enhancing pod density and compute efficiency.
-
Mitigate IP Exhaustion:
- Plan for Growth:
- Size VPCs and subnets with growth in mind to prevent IP exhaustion.
- Consider using
/19subnets for the majority of workload types.
- Use IPv6 (Recommended):
- Adopt IPv6 to work around RFC1918 limitations and provide a larger IP address space.
- Enables pods and services to receive IPv6 addresses while maintaining compatibility with IPv4 endpoints.
- Expand IP Space with Custom Networking:
- Use non-routable secondary CIDRs (e.g.,
100.64.0.0/10,198.19.0.0/16) to conserve routable IPs.
- Use non-routable secondary CIDRs (e.g.,
- Optimize the Warm Pool of IPs:
- Configure environment variables like
WARM_IP_TARGET,MINIMUM_IP_TARGET, andWARM_ENI_TARGETto match the number of pods expected on nodes. - Adjust these values to maintain an optimal warm IP pool without causing excessive EC2 API calls.
- Configure environment variables like
- Monitor IP Address Inventory:
- Use CNI Metrics Helper to monitor metrics like the number of ENIs, IP addresses assigned to pods, and available IP addresses.
- Set CloudWatch alarms for IP address inventory monitoring.
- Plan for Growth:
-
Other Architectural Patterns:
- Optimize communication across VPCs.
- Share a VPC across multiple accounts to limit IPv4 address allocation.
- Learn more about these patterns in resources like "Designing hyperscale Amazon VPC networks" and "Build secure multi-account multi-VPC connectivity with Amazon VPC Lattice."
Do these and you will:
- optimize IP address utilization,
- mitigate IP exhaustion,
- and ensure efficient and scalable networking for your EKS clusters.