Deploying LLM to SageMaker (manually)
These are notes for working out the steps and process for deploying an LLM to SageMaker as part of my YouTube video series, hence they will be rough, but I will include the link to the completed video.
Agenda
In this first video, we'll focus on the end-to-end deployment process. We'll cover:
- Preparing the LLM model for deployment
- Writing the inference code to handle requests
- Launching the model endpoint on SageMaker
Deployment Overview
Key components
- model artefacts
- inference code
- Endpoint (sagemaker)
Tasks at a high level
- prepare the model files, upload to S3
- write some inference code, package with deps
- create SM model using the model package
- launch Endpoint to servce model.
Prepare LLM
Model Theory
According to the SageMaker documentation, the model directory should have the following structure:
/model.tar.gz
├── model.pth
├── code/
│ ├── inference.py
│ ├── requirements.txt
Here's what each component represents:
model.pth: This is the serialized model file containing the trained weights of your PyTorch model.code/: This directory contains the necessary code files for the inference script.inference.py: This is the inference script that we'll discuss later, containing themodel_fn,input_fn,predict_fn, andoutput_fnfunctions.requirements.txt: This file lists the dependencies required by your inference script, such as thetorchandtransformerslibraries.
Example Stable Diffusion XL
On my SageMaker instance, I deployed SDXL, from the terminal here's what the artefacts look like:
sagemaker-user@default:~/model-58101$ ls -ll
total 92
-rw-r--r-- 1 sagemaker-user users 12506 Mar 7 04:03 README.md
drwxr-xr-x 3 sagemaker-user users 76 Mar 7 04:05 code
drwxr-xr-x 2 sagemaker-user users 38 Mar 7 04:04 feature_extractor
-rw-r--r-- 1 sagemaker-user users 543 Mar 7 04:03 model_index.json
drwxr-xr-x 2 sagemaker-user users 50 Mar 7 04:04 safety_checker
drwxr-xr-x 3 sagemaker-user users 61 Mar 7 04:04 scheduler
drwxr-xr-x 2 sagemaker-user users 50 Mar 7 04:04 text_encoder
drwxr-xr-x 2 sagemaker-user users 102 Mar 7 04:04 tokenizer
drwxr-xr-x 2 sagemaker-user users 60 Mar 7 04:04 unet
-rw-r--r-- 1 sagemaker-user users 71237 Mar 7 04:03 v1-variants-scores.jpg
drwxr-xr-x 2 sagemaker-user users 60 Mar 7 04:04 vae
sagemaker-user@default:~/model-58101$
looking in code:
sagemaker-user@default:~/model-58101/code$ ls -ll
total 8
-rw-r--r-- 1 sagemaker-user users 1170 Mar 7 03:57 inference.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 sagemaker-user users 38 Mar 7 03:57 requirements.txt
and the default inference.py file that comes default
import base64
import torch
from io import BytesIO
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
def model_fn(model_dir):
# Load stable diffusion and move it to the GPU
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_dir, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
return pipe
def predict_fn(data, pipe):
# get prompt & parameters
prompt = data.pop("inputs", data)
# set valid HP for stable diffusion
num_inference_steps = data.pop("num_inference_steps", 50)
guidance_scale = data.pop("guidance_scale", 7.5)
num_images_per_prompt = data.pop("num_images_per_prompt", 4)
# run generation with parameters
generated_images = pipe(
prompt,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_images_per_prompt=num_images_per_prompt,
)["images"]
# create response
encoded_images = []
for image in generated_images:
buffered = BytesIO()
image.save(buffered, format="JPEG")
encoded_images.append(base64.b64encode(buffered.getvalue()).decode())
# create response
return {"generated_images": encoded_images}
Prepare LLM Model
Fetch pre-trained, open source GPT-Neo model, from Hugging Face.
Download LLM from HuggingFace
a few options
- programmatically e.g.
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM - git e.g.
git lfs install && gti clone https://huggingface.co/distilgpt2
On the HuggingFace model repo page,
I'm going with git so need to install lfs or
# install
sudo apt install git-lfs
# enable
git lfs install
pull GPT-NeoX-20b down
~/Repositories ❯ git clone https://huggingface.co/EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b
Cloning into 'gpt-neox-20b'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 125, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (125/125), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (114/114), done.
remote: Total 125 (delta 12), reused 121 (delta 10), pack-reused 0
Receiving objects: 100% (125/125), 1.14 MiB | 1.69 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (12/12), done.
Filtering content: 100% (93/93), 76.91 GiB | 24.04 MiB/s, done.
Damn, you can see there ^ the model is 76.91 GiB.
gpt-neox-20b i.e. 20 Billion parameter LLM included 46 pytorch bin files, which Claude explained looks like the LLM is sharded cos of the size, so I would have to try to either a) merge all bins or b) ensure the inference script was prepped to load all the shards first.
I'm going to leave this and look for a smaller, simpler model to learn on first, and will come back to this later.
Going with the GPT-125M LLM instead
~/Repositories ❯ git clone https://huggingface.co/EleutherAI/gpt-neo-125m
Cloning into 'gpt-neo-125m'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 65, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (7/7), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (7/7), done.
remote: Total 65 (delta 2), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 58
Unpacking objects: 100% (65/65), 1.11 MiB | 2.23 MiB/s, done.
Filtering content: 100% (4/4), 1.93 GiB | 21.55 MiB/s, done.
the file list of r gpt-neo-125m looks more manageable and not sharded
~/R/gpt-neo-125m on main ❯ ll
total 1.3G
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 1007 Apr 2 19:01 config.json
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 478M Apr 2 19:03 flax_model.msgpack
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 119 Apr 2 19:01 generation_config.json
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 446K Apr 2 19:01 merges.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 502M Apr 2 19:03 model.safetensors
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 502M Apr 2 19:03 pytorch_model.bin
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 4.1K Apr 2 19:01 README.md
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 502M Apr 2 19:03 rust_model.ot
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 357 Apr 2 19:01 special_tokens_map.json
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 727 Apr 2 19:01 tokenizer_config.json
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 2.1M Apr 2 19:01 tokenizer.json
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 878K Apr 2 19:01 vocab.json
Organise Model Artefacts
I used Claude 3 Opus (paid) to generate the steps for me, and I just tweak any minor issues until it's working.
Create a new directory for your model (e.g., gpt-neo-125m-model).
Copy the following files from the gpt-neo-125m model repository into the gpt-neo-125m-model directory:
config.json: This file contains the model configuration parameters.pytorch_model.bin: This file contains the pretrained model weights for PyTorch.tokenizer.json: This file contains the tokenizer configuration.special_tokens_map.json: This file contains the mappings for special tokens.vocab.json: This file contains the vocabulary used by the tokenizer.merges.txt: This file contains the byte-pair encoding (BPE) merges used by the tokenizer.
Create a requirements.txt file in the gpt-neo-125m-model directory and specify the dependencies required for your model. For example:
transformers==4.12.0
torch==1.9.0
Adjust the versions based on your specific requirements and compatibility.
Create a code/ directory in the gpt-neo-125m-model directory and place any custom inference code or scripts you have written there. For example, you can create a inference.py file with the following content:
import json
import torch
from transformers import GPTNeoForCausalLM, GPT2Tokenizer
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
def model_fn(model_dir):
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained(model_dir)
model = GPTNeoForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_dir)
model.to(device)
model.eval()
return model, tokenizer
def input_fn(serialized_input_data, content_type):
if content_type == "application/json":
input_data = json.loads(serialized_input_data)
text = input_data["text"]
return text
raise Exception("Unsupported content type: {}".format(content_type))
def predict_fn(input_data, model_and_tokenizer):
model, tokenizer = model_and_tokenizer
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(input_data, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
output = model.generate(input_ids, max_length=100, num_return_sequences=1)
generated_text = tokenizer.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
return generated_text
def output_fn(prediction, accept):
if accept == "application/json":
return json.dumps({"generated_text": prediction}), accept
raise Exception("Unsupported accept type: {}".format(accept))
Review code:
model_fn(model_dir): This function is called by SageMaker to load the model. It takes the model_dir as input, which is the directory where the model files are stored. In this function, you load the tokenizer and the model, move the model to the appropriate device (CPU or GPU), and return the model and tokenizer.input_fn(serialized_input_data, content_type): This function is called by SageMaker to deserialize the input data. It takes the serialized input data and the content type as input. In this example, it expects the input data to be in JSON format with a "text" key containing the input text. You can modify this function to handle different input formats based on your requirements.predict_fn(input_data, model_and_tokenizer): This function is called by SageMaker to perform the actual prediction. It takes the deserialized input data and the loaded model and tokenizer as input. In this example, it encodes the input text using the tokenizer, generates text using the model, and decodes the generated output.output_fn(prediction, accept): This function is called by SageMaker to serialize the prediction output. It takes the prediction and the desired output content type as input. In this example, it returns the generated text as a JSON response.
Package Deployment Model
Your directory should look like this:
~/Repositories/SM-gpt-neo-125m/gpt-neo-125m-model ❯ ll
total 332M
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 1007 Apr 2 21:41 config.json
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 1.2K Apr 2 22:02 inference.py
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 446K Apr 2 21:41 merges.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 502M Apr 2 21:40 pytorch_model.bin
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 34 Apr 2 21:55 requirements.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 357 Apr 2 21:41 special_tokens_map.json
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 727 Apr 2 21:41 tokenizer_config.json
-rw-rw-r-- 1 rxhackk rxhackk 878K Apr 2 21:41 vocab.json
create a sub-dir, and organise your files like this:
~/Repositories/SM-gpt-neo-125m/gpt-neo-125m-model ❯ tree at 23:22:04
.
├── code
│ ├── inference.py
│ └── requirements.txt
├── config.json
├── merges.txt
├── pytorch_model.bin
├── special_tokens_map.json
├── tokenizer_config.json
└── vocab.json
1 directory, 8 files
Compress the entire gpt-neo-125m-model directory into a tar.gz file using a command like:
# change into the model dir, where the `code/` subdir is
cd gpt-neo-125m-model
tar -czf gpt-neo-125m-model.tar.gz *
You now have a file gpt-neo-125m-model.tar.gz that contains the necessary files for deploying the gpt-neo-125m model to SageMaker.
Deploy Model to SageMaker
Model is ready for upload, and then a SageMaker model using our "custom" LLM.
Upload to s3
Upload the gpt-neo-125m-model.tar.gz file to an S3 bucket.
~/Repositories/SM-gpt-neo-125m ❯ aws s3 cp gpt-neo-125m-model.tar.gz s3://ra-aws-s3-lab ✘ 252 at 22:11:03
upload: ./gpt-neo-125m-model.tar.gz to s3://ra-aws-s3-lab/gpt-neo-125m-model.tar.gz
Create Role
cos I'm lazy, I got the aws cli commands to do this from the terminal:
create assume-role-policy.json to service-link our role:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "sagemaker.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
create role: aws iam create-role --role-name SageMakerExecutionRole --assume-role-policy-document file://assume-role-policy.json
output:
{
"Role": {
"Path": "/",
"RoleName": "SageMakerExecutionRole",
"RoleId": "AROA4EFKKWBQIC4MCQHWD",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::REDACTED:role/SageMakerExecutionRole",
"CreateDate": "2024-04-02T09:49:20+00:00",
"AssumeRolePolicyDocument": {
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "sagemaker.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
}
}
attach the SageMakerFullAccess policy: aws iam attach-role-policy --role-name SageMakerExecutionRole --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonSageMakerFullAccess
output: N/A
get the ARN cos I need it for my deployment code: aws iam get-role --role-name SageMakerExecutionRole --query 'Role.Arn' --output text
output:
arn:aws:iam::REDACTED:role/SageMakerExecutionRole
These create role commands were successful, but when running my deploy.py code, I ran into s3 permissions.
add AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess to get s3:GetObject permissions for my role: aws iam attach-role-policy --role-name SageMakerExecutionRole --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess
Create Endpoint
Use the SageMaker Python SDK to create the "SageMaker Model".
Now, according to Claude, you can run this code in a number of places, it doesn't matter, it will call the SageMaker API and stand up this model. You can call it locally (note: you need pip install sagemaker), or in a JupyterLab notebook, or AWS Cloud9.
I'm going to try to call it locally, the following code I put into deploy.py:
from sagemaker.pytorch import PyTorchModel
model_data = "s3://ra-aws-s3-lab/gpt-neo-125m-model.tar.gz"
role = "arn:aws:iam::REDACTED:role/SageMakerExecutionRole"
pytorch_model = PyTorchModel(
model_data=model_data,
role=role,
framework_version="1.9.0",
py_version="py38",
entry_point="inference.py"
)
predictor = pytorch_model.deploy(
instance_type="ml.m5.large",
initial_instance_count=1,
)
Success!
there was a bunch of troubleshooting that happened before this stood up, and notes have been updated retroactively, but I've tried to capture what came out of the original process.
~/Repositories/SM-gpt-neo-125m ❯ python3 deploy.py at 23:43:51
sagemaker.config INFO - Not applying SDK defaults from location: /etc/xdg/xdg-ubuntu/sagemaker/config.yaml
sagemaker.config INFO - Not applying SDK defaults from location: /home/rxhackk/.config/sagemaker/config.yaml
----------!%
~/Repositories/SM-gpt-neo-125m ❯ took 14m 1s at
⏱️ 14mins to deploy.
Check AWS Console
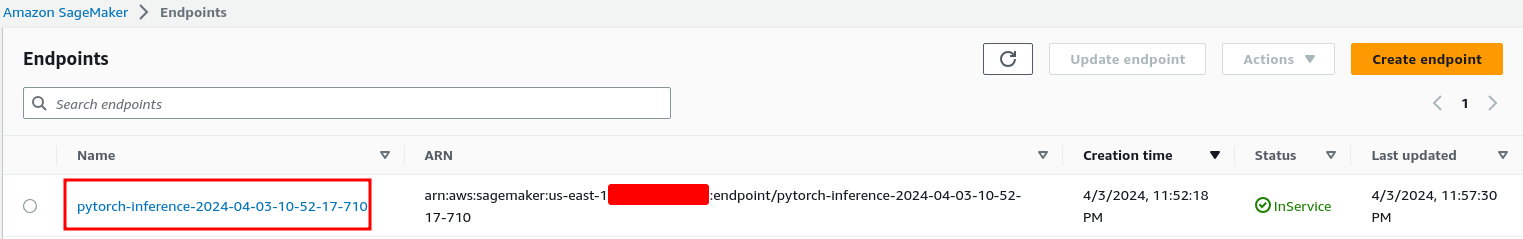
Test the Endpoint
The moment of truth!
Now the custom model is up & running and our inference endpoint says "✅InService" we should be able to invoke it and get the inference script workingf:
aws sagemaker-runtime invoke-endpoint \
--endpoint-name my-endpoint \
--cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out \
--body '{"text": "Hello, LLM!"}' \
--content-type application/json output.txt
I need my new endpoint name. I can get it via AWS Console, or use cli to grab it,:
To get ALL info:
aws sagemaker list-endpoints
To get just EndpointName in a table:
aws sagemaker list-endpoints \
--query "Endpoints[*].[EndpointName]" \
--output table
output
-----------------------------------------------------------
| ListEndpoints |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| pytorch-inference-2024-04-03-10-52-17-710 |
| huggingface-pytorch-inference-2024-03-07-04-18-07-114 |
| DEMO-1709699475-cbc3-endpointx |
| SDXL-v2-1-RAMOS |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
(END)
Invoke
aws sagemaker-runtime invoke-endpoint \
--endpoint-name pytorch-inference-2024-04-03-10-52-17-710 \
--cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out \
--body '{"text": "Hi, LLM!"}' \
--content-type application/json output.txt
response:
{
"ContentType": "application/json",
"InvokedProductionVariant": "AllTraffic"
}
(END)
✅ We have a output.txt file now from our LLM
❯ cat output.txt took 44s at 11:58:49
{"generated_text": "Hi, LLM!\n\nI'm a little confused about the word \"soul\" in the English language. I'm not sure what the word means in the English language, but I'm not sure what the word means in the English language. I'm not sure what the word means in the English language. I'm not sure what the word means in the English language. I'm not sure what the word means in the English language. I'm not sure what the word means in the"}%
Done.
Bonus: Re-Deploy Updates to your SageMaker Endpoint
I needed to update my inference.py script to the following, to get better results:
...
def predict_fn(input_data, model_and_tokenizer):
model, tokenizer = model_and_tokenizer
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(input_data, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
output = model.generate(
input_ids,
max_length=150,
num_return_sequences=1,
temperature=0.7,
top_k=50,
top_p=0.95
)
generated_text = tokenizer.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
return generated_text
...
so the whole inference.py now reads
import json
import torch
from transformers import GPTNeoForCausalLM, GPT2Tokenizer
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
def model_fn(model_dir):
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained(model_dir)
model = GPTNeoForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_dir)
model.to(device)
model.eval()
return model, tokenizer
def input_fn(serialized_input_data, content_type):
if content_type == "application/json":
input_data = json.loads(serialized_input_data)
text = input_data["text"]
return text
raise Exception("Unsupported content type: {}".format(content_type))
def predict_fn(input_data, model_and_tokenizer):
model, tokenizer = model_and_tokenizer
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(input_data, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
output = model.generate(
input_ids,
max_length=150,
num_return_sequences=1,
temperature=0.7,
top_k=50,
top_p=0.95
)
generated_text = tokenizer.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
return generated_text
def output_fn(prediction, accept):
if accept == "application/json":
return json.dumps({"generated_text": prediction}), accept
raise Exception("Unsupported accept type: {}".format(accept))
retar it, re-upload to s3.
Redeploy SageMaker Model
Here's the trick to de-deploying the same endpoint, you just need to add this to the existing deploy.py
# original code
from sagemaker.pytorch import PyTorchModel
model_data = "s3://ra-aws-s3-lab/gpt-neo-125m-model.tar.gz"
role = "arn:aws:iam::REDACTED:role/SageMakerExecutionRole"
pytorch_model = PyTorchModel(
model_data=model_data,
role=role,
framework_version="1.9.0",
py_version="py38",
entry_point="inference.py"
)
predictor = pytorch_model.deploy(
instance_type="ml.m5.large",
initial_instance_count=1,
# add this oneline
update_endpoint=True
)
Run re-deploy: python3 deploy.py
~/Repositories/SM-gpt-neo-125m ❯ python3 deploy.py at 16:08:03
sagemaker.config INFO - Not applying SDK defaults from location: /etc/xdg/xdg-ubuntu/sagemaker/config.yaml
sagemaker.config INFO - Not applying SDK defaults from location: /home/rxhackk/.config/sagemaker/config.yaml
-
--------!%
~/Repositories/SM-gpt-neo-125m ❯ took 13m 40s
only took ⏱️ 13m40s this time.
check endpoints: aws sagemaker list-endpoints --query "Endpoints[*].[EndpointName]" --output table
looks like its actually stop up a different endpoint:
-----------------------------------------------------------
| ListEndpoints |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| pytorch-inference-2024-04-04-03-16-43-017 |
| pytorch-inference-2024-04-03-10-52-17-710 |
| huggingface-pytorch-inference-2024-03-07-04-18-07-114 |
| DEMO-1709699475-cbc3-endpointx |
| SDXL-v2-1-RAMOS |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
(END)
picking the new endpoint in our invoke method
aws sagemaker-runtime invoke-endpoint \
--endpoint-name pytorch-inference-2024-04-04-03-16-43-017 \
--cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out \
--body '{"text": "Hi! how are you?"}' \
--content-type application/json \
output.txt
new output, but probably just as sh! as the previous, think it needs a lot more config attention, but that's for another post.
cat output.txt
{"generated_text": "Hi! how are you?\n\nI'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm back! I'm"}%
Troubleshooting
python3 deploy.py
Deploying the *.tar.gz model package from s3.
Error:
botocore.exceptions.ClientError: An error occurred (ValidationException) when calling the CreateModel operation: Could not access model data at s3://ra-aws-s3-lab/gpt-neo-125m-model.tar.gz. Please ensure that the role "arn:aws:iam::REDACTED:role/SageMakerExecutionRole" exists and that its trust relationship policy allows the action "sts:AssumeRole" for the service principal "sagemaker.amazonaws.com". Also ensure that the role has "s3:GetObject" permissions and that the object is located in us-east-1. If your Model uses multiple models or uncompressed models, please ensure that the role has "s3:ListBucket" permission.
I have double checked my IAM Role, according to each comment in the error message, and my Role is legit. I even tested by attaching Administrator access to the role, and it got the same error.
After reading SageMaker Python Docs I saw my deploy.py was missing an entry_point.
Solution: I changed this
pytorch_model = PyTorchModel(
model_data=model_data,
role=role,
framework_version="1.9.0",
py_version="py38"
)
to this
pytorch_model = PyTorchModel(
model_data=model_data,
role=role,
framework_version="1.9.0",
py_version="py38",
entry_point="inference.py"
)
And the IAM Role error went away 😒 ✅
I don't know why a missing parameter for pytorch model setup has to do with tripping on an IAM Role, maybe that's just python 🤷.
No such file or directory: 'inference.py'
error message:
sagemaker.config INFO - Not applying SDK defaults from location: /etc/xdg/xdg-ubuntu/sagemaker/config.yaml
sagemaker.config INFO - Not applying SDK defaults from location: /home/rxhackk/.config/sagemaker/config.yaml
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/rxhackk/Repositories/SM-gpt-neo-125m/deploy.py", line 14, in <module />
predictor = pytorch_model.deploy(
File "/home/rxhackk/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sagemaker/model.py", line 1610, in deploy
self._create_sagemaker_model(
File "/home/rxhackk/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sagemaker/model.py", line 865, in _create_sagemaker_model
container_def = self.prepare_container_def(
File "/home/rxhackk/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sagemaker/pytorch/model.py", line 319, in prepare_container_def
self._upload_code(deploy_key_prefix, repack=self._is_mms_version())
File "/home/rxhackk/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sagemaker/model.py", line 763, in _upload_code
utils.repack_model(
File "/home/rxhackk/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sagemaker/utils.py", line 548, in repack_model
_create_or_update_code_dir(
File "/home/rxhackk/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/sagemaker/utils.py", line 609, in _create_or_update_code_dir
shutil.copy2(inference_script, code_dir)
File "/usr/lib/python3.10/shutil.py", line 434, in copy2
copyfile(src, dst, follow_symlinks=follow_symlinks)
File "/usr/lib/python3.10/shutil.py", line 254, in copyfile
with open(src, 'rb') as fsrc:
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'inference.py'
Solution: for me this was due to an incorrect directory strucuture for the model package I created in Package Deployment Model (my original instructions, which I've fixed, but this was the step I borked this in).
Make sure you tar just the contents of the model package directory and not create a parent directory, i.e. when you untar or view the archive, you should see the code/ directory (where the inference code is) straight away.
Invalid base64
Got this error:
~/Repositories/SM-gpt-neo-125m ❯ aws sagemaker-runtime invoke-endpoint \ ✘ 254 at 11:52:01
--endpoint-name pytorch-inference-2024-04-03-10-52-17-710 \
--body '{"text": "Hi, LLM!"}' \
--content-type application/json output.txt
Invalid base64: "{"text": "Hi, LLM!"}"
I asked Claude3 and got these solutions:
aws sagemaker-runtime invoke-endpoint \ ✘ 255 at 11:52:39
--endpoint-name pytorch-inference-2024-04-03-10-52-17-710 \
--body $(echo '{"text": "Hi, LLM!"}' | base64) \
--content-type application/json \
output.txt
✅ works.
aws sagemaker-runtime invoke-endpoint \
--endpoint-name pytorch-inference-2024-04-03-10-52-17-710 \
--cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out \
--body '{"text": "Hi, LLM!"}' \
--content-type application/json \
output.txt
✅ works.